- AI
- 15 min read
- June 2023
Will Generative AI Tools Replace the Human Workforce?
In the expanding universe of artificial intelligence (AI), a new star shines brightly: Generative AI tools. From its humble beginnings as a concept etched on research papers, generative AI has evolved into an invaluable tool, reshaping industries' operations and transforming how we work.
This article delves into the workings of Generative AI tools, their current implementation in the workforce, potential impacts, limitations, and their probable influence on the future of work. As we embark on this journey, we aim to understand the capabilities, applications, and concerns surrounding generative AI.
Examples of generative AI tools
Generative AI, wielding machine learning algorithms, has the uncanny ability to sift through mounds of data, learn from it, and then conjure up fresh content. This magic wand can be waved to create anything from news articles to stock photography. Here's a peek into some of the fascinating generative AI tools available today, including ChatGPT, Google's Bard, and others.
1. ChatGPT: The conversational whiz
Developed by OpenAI, ChatGPT is a natural language processing chatbot that's a pro at deciphering prompts and offering responses that could fool you into thinking you're chatting with a human.
Its training regime involved devouring diverse content from the internet. It can handle straightforward queries like "Who signed the Declaration of Independence?" or take on more intricate tasks such as bug hunting in code.
However, one must remember that ChatGPT's knowledge repository only goes up to 2021, and it can sometimes spin false answers that might seem deceivingly accurate.
2. DALL-E: The imaginative illustrator
DALL-E, another brainchild of OpenAI, uses natural language processing to create original images.
A user can give DALL-E a prompt, and voila! A detailed image appears within seconds. Whether you want an image of "a simple sunset" or a more complex "watercolor-style fall sunset landscape featuring purples and oranges," DALL-E covers you.
Its creations are used in various applications, from book covers to stock photographs for websites.
3. LaMDA: The smooth talker
Google LaMDA, an acronym for "language model for dialogue applications," is built to engage users in authentic conversations.
It understands the context of a conversation and reciprocates with human-like dialogue. It rides on Transformers, a neural network invented by Google trained to comprehend words and their relational nuances in conversations.
LaMDA powers Google Bard, a conversational AI chatbot akin to ChatGPT.
4. Google Bard: The Enhanced Conversationalist
Following the footsteps of OpenAI's ChatGPT, Google has developed its own innovative AI, known as Google Bard, by integrating the prowess of Google Search directly into the conversational model.
Google Bard has significantly transformed the way chatbots operate, turning the conventional paradigm on its head.
Google Bard does not rely solely on pre-trained language models. Instead, its extraordinary feature lies in its capacity to actively draw on Google's massive web database for up-to-date, pertinent information.
It retrieves and processes information from the web in real-time during the conversation, thus ensuring that the responses provided are current, relevant, and comprehensive.
5. Bing AI: The New Contender
Bing AI, the search engine by Microsoft, might not have beaten Google in popularity. Still, in 2023, Microsoft unveiled a new avatar of Bing, equipped with an AI chatbot that provides answers alongside search results.
Bing AI operates similarly to ChatGPT and Google Bard and was developed using GPT-4 (generative pre-trained transformer 4), the latest large language model from OpenAI.
Recommended reading: Generative AI Tools in the Creative Domains: The Power and Pressure Game Is On!
What jobs will AI replace?
The top 10 jobs most likely to be replaced by AI
- Entry-level
- Admin Roles
- Data Entry Clerks
- Software Engineers and Coders
- Customer Service Reps
- Paralegals
- Copywriters and Content Roles
- Graphic Designers
- Bankers and Accountants
- Traders
- Fact-Checkers and Proofreaders
The public's biggest concern: Will AI replace me or my colleagues?
The question of AI displacing jobs is not one of overnight revolution but of an evolving landscape where the integration of AI in the workforce has become increasingly tangible.
In its 2020 report, the World Economic Forum forecasted that AI might replace 85 million jobs by 2025. However, Mckinsey's slightly more restrained prediction in 2021 suggested a figure closer to 45 million by 2030.
Our studies at Rapidops indicate that almost half of the business leaders surveyed would contemplate utilizing AI as a substitute for new hires within their organizations.
In light of the meteoric rise in the popularity of AI, like ChatGPT, Goldman Sachs has predicted that approximately 300 million jobs could potentially be automated or replaced by AI in the foreseeable future.
AI can accomplish specific tasks within job descriptions rather than replacing entire roles. Nevertheless, it's not far-fetched to envision a future where AI supplants complete roles.
Instead of picturing a scenario where entire jobs vanish overnight, replaced by AI like ChatGPT, a more probable outlook for the upcoming years involves AI being leveraged to assist a growing segment of the workforce in their tasks.
A recent paper by OpenAI suggests that AI could soon aid approximately 10% of tasks for eight out of every ten workers. Moreover, around 19% of the workforce might be able to employ AI to complete half of their tasks. This distribution indicates that AI's role in job displacement will likely be a steady, progressive transition rather than a sudden overhaul.
Is AI taking over jobs or creating more?
According to a 2022 Gartner survey, an overwhelming 80% of corporate leaders proposed a universal application of AI, signifying that automation may pervade every conceivable corner of the private sector, leaving no facet untouched.
Dialogues revolving around the influence of artificial intelligence and advanced robotics on the employment landscape have predominantly concentrated on the roles they're poised to take over.
Yet, the progression of AI holds the promise of spawning an entirely new sector brimming with employment opportunities. It is far from a one-sided situation.
As highlighted in a previously referenced World Economic Forum report, the advent of AI, while potentially rendering approximately 85 million jobs redundant, is also predicted to forge an impressive 97 million novel positions.
Complementary studies like one conducted by the University of Warwick and unveiled in March of the previous year unearthed that investments in AI were 28.4% more likely to stimulate job creation than investments in other analogous technologies.
Contrary to the prevailing notion that AI's potential impact on jobs primarily pertains to potential job losses as AI acquires the ability to automate intricate tasks, the research underscores that AI is equally likely to precipitate net job creation in companies integrating AI as it is to instigate net job losses.
Advantages of generative AI: how it can benefit you
Generative AI is important for several reasons. Some of the key benefits of generative AI include:
1. Novel content creation
Generative AI can produce original content that mirrors human-created material, encompassing images, videos, and text. These tools have become increasingly advanced, enabling applications like an AI paragraph generator to craft high-quality text content across different tones and styles. Whether for creative writing, marketing copy, or informative articles, these generators streamline the content creation process, offering a novel approach to generating unique and engaging material efficiently.
2. Enhancing efficiency and accuracy of present AI systems
Generative AI algorithms can potentially augment the performance of existing AI systems, including natural language processing and computer vision. One noteworthy application is the generation of synthetic data, which can be leveraged to train and fine-tune other AI algorithms, enhancing their efficiency and accuracy.
3. Unearthing hidden insights from complex data
Generative AI can enable novel ways to explore and analyze complex data. By leveraging these algorithms, businesses and researchers can discover concealed patterns and trends that might not be immediately apparent from unprocessed data. This can facilitate more informed decision-making and yield unexpected insights.
4. Automating and accelerating business processes
Generative AI algorithms can effectively automate and expedite numerous tasks and processes. This leads to considerable time and resource savings and enhances operational efficiency for businesses and organizations.
The potential dangers of generative AI
Generative AI systems like ChatGPT have revolutionized our interface with artificial intelligence, transforming fields such as writing, programming, and job application processes. However, the potential benefits come with a range of considerable risks.
Some countries have even banned ChatGPT or revisited AI policies to ensure user safety due to concerns about trust and security. Let’s dive deeper.
1. AI hallucinations
AI hallucinations refer to the inaccuracies or errors that can occur in AI outputs. Although these models are sophisticated, they're not infallible and depend heavily on their training data to form responses.
Such errors are often seen in AI chatbots, where misunderstandings and incorrect replies can occur. Training data can sometimes lead to biased or factually incorrect responses, which can be problematic when people depend on these systems for information.
2. Deepfakes
Deepfakes are a disturbing application of generative AI. They use this technology to create hyper-realistic but false videos, photos, and voice recordings that mimic real people.
Deepfakes have led to several viral incidents, such as a fabricated image of Pope Francis in a puffer jacket and an AI-created song in the style of Drake and the Weeknd.
3. Data privacy concerns
Data privacy is another significant concern with generative AI. User data, frequently used for model training, can potentially compromise privacy. Some instances have led to bans on AI systems in countries due to the lack of legal authority to collect user data.
This also raises the data storage and confidentiality question, as these applications may indefinitely store user input information and use it to train other models.
4. Cybersecurity threats
The advanced abilities of generative AI models can lead to cybersecurity threats if mishandled. For instance, these tools could be used to create malicious code or develop more sophisticated social engineering and phishing attacks.
While AI system providers generally assure customers of robust security measures, there often isn't a way for users to independently verify these safety features.
5. Copyright infringement
Copyright issues arise due to the nature of generative AI model training, which utilizes large amounts of internet data. This process could potentially use works protected by copyright to generate new content, causing particular issues with AI-generated art, including music and images.
The ambiguity surrounding the exact training data used further complicates these copyright concerns.
Looking Ahead: The future of Generative AI and the human workforce
In its 2019 survey, McKinsey asked companies about their AI adoption, and 58% of respondents revealed they had embedded AI in at least one business function.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has the potential to significantly reshape our labor market, leaving scarcely any profession unaffected, be it agriculture or security.
It can augment some jobs, making them more effective, while replacing others entirely and simultaneously stimulating the birth of novel roles and industries.
However, this transformation isn't set in stone, and with appropriate strategies, the workforce can be prepared to adapt to these shifts.
As we transition into a new epoch, where Generative AI tools and the human workforce coexist, we find ourselves at the crossroads of a transformative journey where careful navigation is crucial for a prosperous future.
The intertwining of AI and human effort in the workplace isn't a tale of conflict but synergy and mutual growth. We envision an equilibrium where AI augments human capabilities, empowers creativity, and boosts productivity while humans, in return, provide the guiding ethical compass and unique emotional intelligence.
To facilitate this harmonious coexistence, several proactive steps need to be taken by organizations:
1. Establishment of AI guidelines and policies
Clear regulations and policies concerning AI usage, data privacy, security, and ethical standards should be drawn up. Effective communication is key to ensuring that all employees understand these guidelines.
2. Employee education and training
Comprehensive training programs are paramount to ensure employees understand how to use AI tools efficiently and safely. Such education extends beyond operational knowledge to incorporate essential legal and ethical considerations.
3. AI governance structures
A well-defined governance system to oversee AI usage is essential. This includes assigning responsibilities, creating clear communication lines, and ensuring checks and balances.
4. Ongoing oversight and monitoring
Implementing robust monitoring processes to ensure AI tools' effective and safe usage, monitoring performance, policy compliance, and potential biases.
5. Fostering collaboration and feedback
Encouraging open dialogue and feedback amongst employees and management. It promotes a culture of continuous learning and collaboration.
6. Ethical guidelines and assessments
Establishing ethical guidelines for AI usage and conducting rigorous ethical impact assessments before deployment can help ensure AI tools align with responsible practices and the company's ethical values.
7. Monitoring for AI bias
Regular audits for bias in AI tools, both during development and after deployment, are necessary to maintain fairness and integrity in AI-driven processes.
8. Transparency and compliance with regulations
Clarifying how AI tools function, make decisions, and utilize data ensures transparency and trust. Additionally, all AI applications must comply with relevant regulations, including data privacy and anti-discrimination laws.
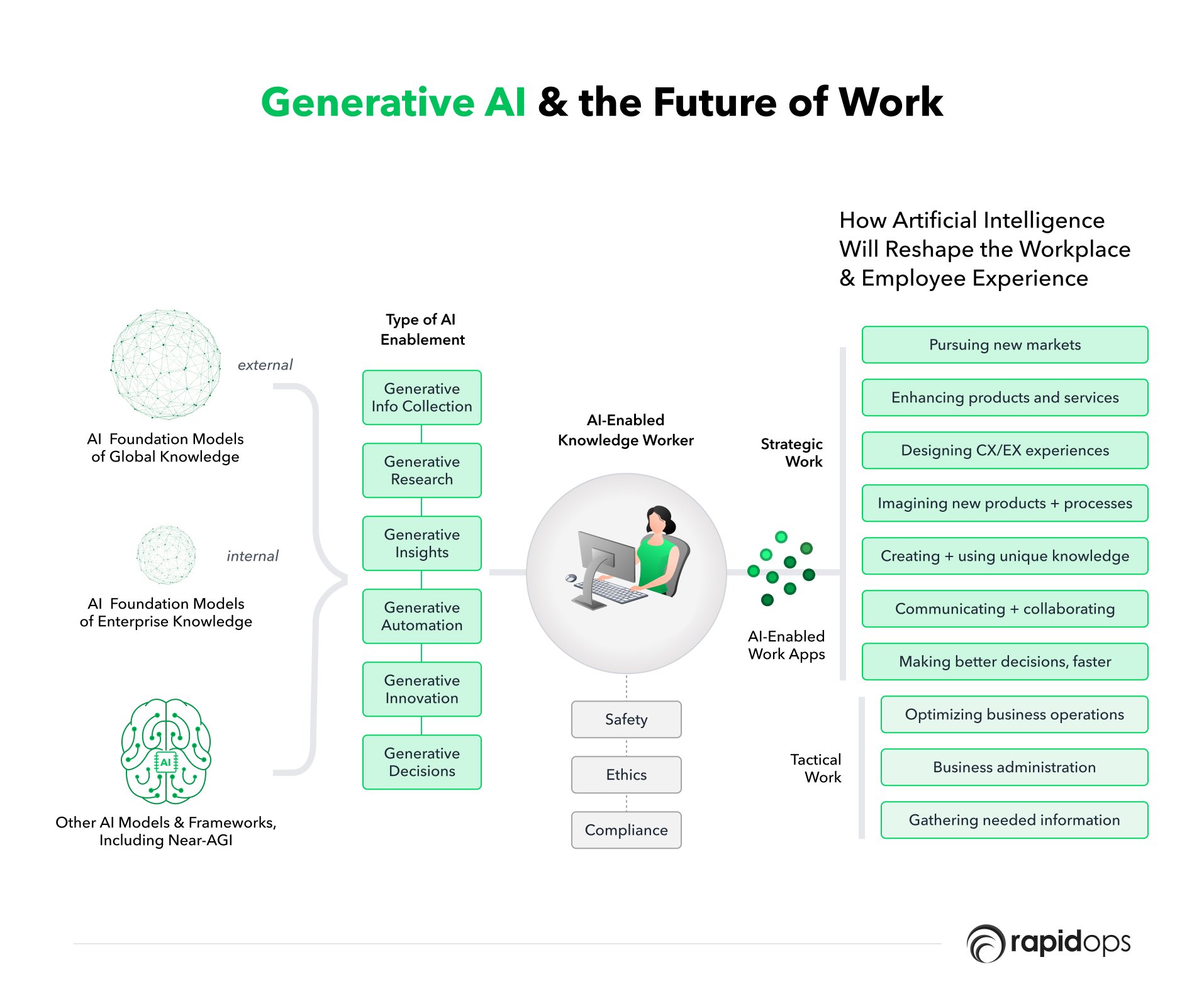
Foundation models, such as large language models (LLMs), can be the cornerstone of AI workplace tools. These are powerful models trained on a vast amount of textual knowledge.
Companies are building upon these models, tailoring them for specific results, or allowing choice for businesses to utilize models they've already vetted.
Prominent LLMs such as AI21's Jurassic-2, Anthropic's Claude, Cohere's LLMs, Google's Pathways Language Model (PaLM), Hugging Face's BLOOM, Meta's LLaMA, NVIDIA's NeMo, OpenAI's GPT-3.5 and GPT-4, are providing compelling results, becoming the backbone for many AI work tools.
9. Leveraging AI as a tool for augmentation
AI can serve as an effective tool to augment many jobs, helping workers become more efficient. Examples can be seen in the education sector, where AI-powered tools like Grammarly assist teachers in grading and improving students' work.
Similarly, tools exist to aid instruction in subjects like mathematics, physics, and foreign languages.
The goal here is not to eliminate the teaching profession but to enhance it with AI's capabilities. This approach can be applied to other complex professions, such as healthcare, creative industries, and software engineering.
10. Strategic workforce redeployment
AI's potential to replace certain jobs, such as cashiers, factory workers, and truck drivers, is apparent. However, this should not be seen solely as a threat but as an opportunity to redirect the workforce toward enhancing customer value.
For example, cashiers in a retail store could be reassigned to roles that involve direct customer interaction, product assistance, cross-selling, or upselling.
11. Reskilling for new job creation
The advent of AI could spur the creation of brand-new roles. While the demand for routine jobs might decline, there will be an increasing need for roles that require critical analysis, strategic planning, and decision-making.
According to the World Economic Forum, many new roles will emerge in sectors such as the care economy, the creator economy, and the green economy.
12. Embracing generative AI tools
A range of Generative AI Tools is available, from text-based tools like GPT-3 and GPT-4, image-based tools like DALL-E and StyleGAN, to sound-based tools like OpenAI's MuseNet, and multi-modal tools like CLIP.
If integrated wisely, these tools can lead to efficiency and innovation in various sectors, paving the way for new opportunities.
13. Investing in skills and knowledge development
Given the potential turbulence and opportunities that AI might bring, there is a critical need for increased skill development and education investment. It's important to equip the current and future workforce with the tools necessary to thrive in an AI-driven economy.
This may involve upskilling for current roles or reskilling to transition into new roles created by the advent of AI.
Take the next step: Embrace the power of generative AI with rapidops
The collaboration between humans and generative AI tools is the key to shaping the future of work. Rather than replacing human workers, generative AI is designed to augment their capabilities, increasing productivity, creativity, and overall business success.
It's crucial to recognize the potential of AI as a powerful tool that relies on human insight and ingenuity for optimal results. If you were worried about AI taking over jobs, we hope this article sheds some light on the subject and helps you resolve the concern.
To navigate this transformative era successfully, partnering with an AI development expert like Rapidops is essential. Our team of experienced professionals, proficient in AI, NLP (Natural Language Processing), and ML (Machine Learning), can provide the expertise and support you need to harness the benefits of generative AI in your organization.
At Rapidops, we are dedicated to exploring innovative approaches and implementing cutting-edge technologies to help businesses achieve their critical objectives.
We will continue to deliver valuable content and insights on the practical application of generative AI and other advanced technologies, ensuring you stay informed and can leverage these advancements in your business operations.
Join us on this exciting journey as we unlock the full potential of AI, driving your organization toward enhanced productivity, innovation, and success. Contact Rapidops today to embark on your AI journey and discover the transformative power of generative AI in your business.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
As generative AI continues to advance and gain prominence, it is natural to have questions about its potential impact on various aspects of society. In this section, we address some frequently asked questions (FAQs) to provide insights into the role of generative AI in the future and its relationship with humanity.
2. What is the future of generative AI?
3. Will AI ever take over humanity?
4. What industries will not be affected by AI?
5. Will AI replace all human jobs in the future?
6. Is AI going to replace everything?
What’s Inside
- Examples of generative AI tools
- What jobs will AI replace?
- Advantages of generative AI: how it can benefit you
- The potential dangers of generative AI
- Looking Ahead: The future of Generative AI and the human workforce
- Take the next step: Embrace the power of generative AI with rapidops
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)




